Backup vs. data archive
Are you looking for a solution to reliably store corporate data? Do you need to store important files for the long term, yet want to access them seamlessly? The choice isn't backup or archive. It's about a smart storage strategy that cost-effectively and legally takes care of one of your company's most important assets: your data.
Archiving
- Compliance: legally compliant and long-term storage of important documents
- Cold data that may not be modified any more
- Moving to secondary storage, protection against deletion and modification
Backup
- Disaster recovery and business continuity: data storage to protect against data loss, e.g. due to technical failures or malware
- Hot data that must be available in the latest version
- Copy on additional data carrier for quick availability in case of loss or damage
The purposes of backup and archiving are fundamentally different. Nevertheless, both processes are closely linked.
- As part of the backup, "hot data" is stored: i.e., current data that is actively being worked with and that must be reliably available. The backup aims to ensure that this data can be restored quickly and that the usual workflows can be resumed after a loss.
- Data archiving is aimed at "cold data", i.e. inactive data that is no longer modified and is hardly ever accessed. Often, this is data that must be stored long-term and unmodifiable for compliance reasons.
Conclusion: If the cold data is not archived, it occupies valuable storage space on expensive primary storage. In addition, it is regularly backed up from the primary storage devices as part of the backup routine, even though it is no longer being used. The cold data then also occupies a lot of storage space on the backup media.
Hierarchical Storage Management (HSM)
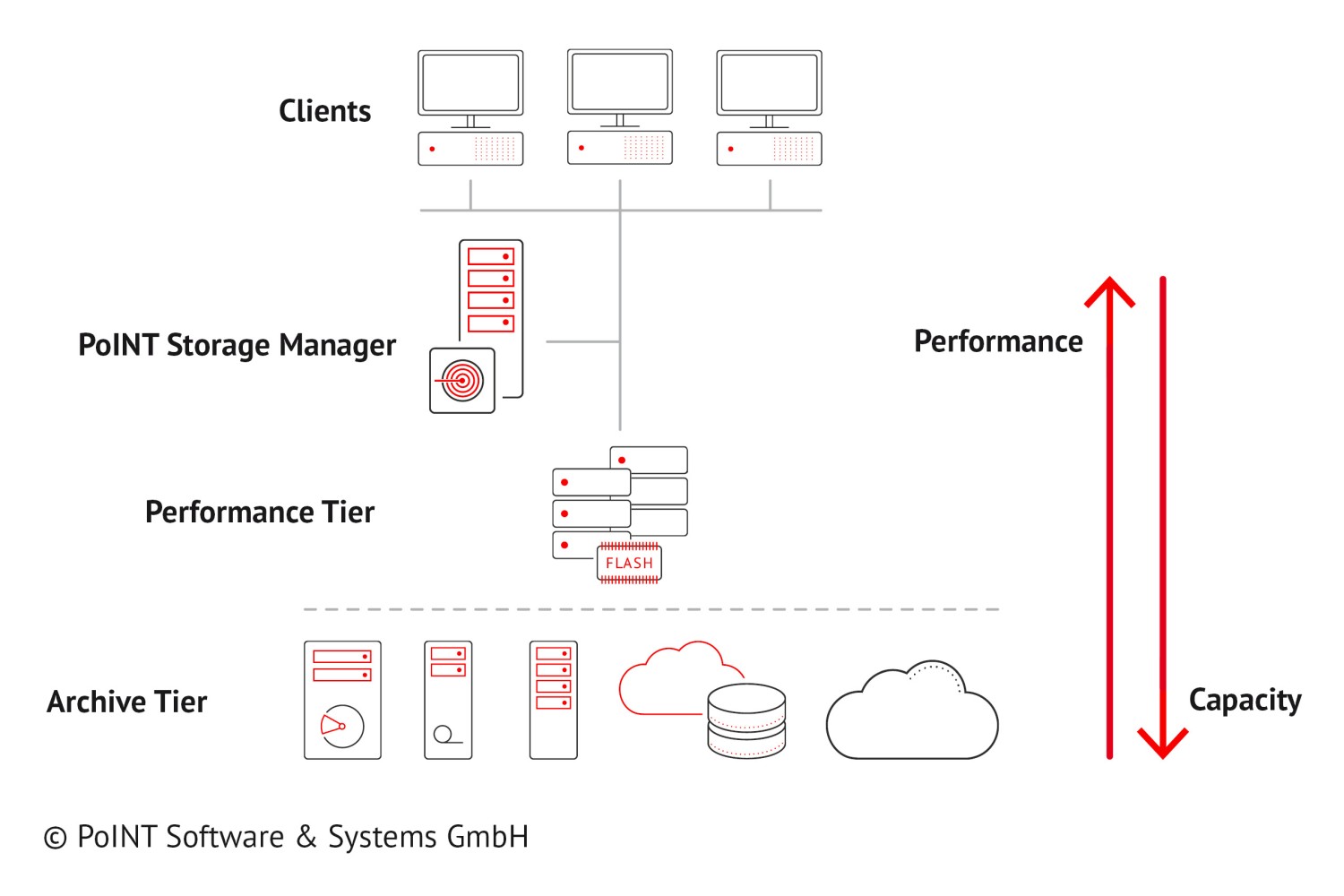
The solution is to optimize the storage infrastructure with hierarchical storage management (HSM).
A two-tier storage architecture consists, for example, of
- fast primary storage, on which the hot data is stored,
- and low-cost secondary storage, on which the cold data is archived.
An appropriate HSM software integrates secondary storage as archive storage. The software stores the data that has not been modified for a specified period of time on the secondary storage.
Hierarchical storage management takes into account the fundamental differences between backup and data archiving. They are adequately represented in a multi-tier storage architecture.
Cost reduction through information lifecycle management
The storage strategy is determined by the so-called Information Lifecycle Management (ILM). ILM takes into account the lifecycle of files: from creation, through the hot and warm phase, to the cold phase. With an ILM strategy, a file is always stored on the storage tier that corresponds to its lifecycle phase.
- Files that have not been used or modified for a longer period of time are displaced to secondary storage.
- Some data sets must be saved in unmodified form for legal or business reasons. They are stored on archive storage with appropriate protection.
Well thought-out information lifecycle management is the basis for optimized and efficient use of storage:
- Relieving primary storage of inactive data
- Reducing the backup load
- Avoiding expensive storage expansions
- More cost-efficient use of existing storage
Automated archiving in accordance with compliance requirements

Software-supported data archiving based on ILM and HSM principles enables cost savings in the storage infrastructure. In addition, automated archiving supports compliance with legal requirements. These require, for example, that archive data must be protected against unintentional deletion and modification.
Appropriate software supports companies in legally compliant archiving.
- The software prevents changes to the archived data.
- It protects the data from premature deletion and thus manages compliance with retention periods.
The archive storage is configured to prevent changes to or deletion of archived data within an appropriately specified period of time. Data retention management of this kind facilitates compliance with the requirements for legally compliant archiving.
Data archiving with PoINT Storage Manager – Archive Edition
PoINT Storage Manager – Archive Edition is a file-based archiving solution that supports companies in meeting their archiving requirements and in fulfilling compliance requirements.
- Automated archiving: PoINT Storage Manager moves your data to secondary storage according to your defined policies and archives the data there with the specified retention times.
- Integrated Retention Management: Electronic documents are retained according to your specifications.
- Protection against modification: Archived files can generally not be modified.
- Transparent access: Archive files are accessed via the primary storage system and the familiar user interface.
- Versioning: If a file is modified in the primary storage, the modified file is stored as a new version in the archive. As a result, all previous versions of a file remain unchanged in the archive.
Automated archiving of cold data in this way reduces the load on primary storage and backups. The storage systems are used more efficiently, and as a result costs are reduced.

![[Translate to en:] Data Sheet PoINT Storage Manager - Archive Edition [Translate to en:] Data Sheet PoINT Storage Manager - Archive Edition](/fileadmin//user_upload/datenblaetter/data-sheet-psm-ae-e-20160822.jpg)




